Data Loss Prevention (DLP) in Microsoft Purview
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a data protection system that prevents data leaks or unauthorized use. DLP policies help maintain the confidentiality of information, including financial documents, personal data, trade secrets, and other critical information.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- How Modern DLP Works
- The Role of Microsoft Purview in Data Protection
- Preparing to Implement DLP: Pre-Implementation Essentials
- Developing a DLP Strategy: Planning for Success
- Preparing Your Environment for DLP Deployment
- Deploying and Fine-Tuning DLP Policies
- Configuring Your DLP Policies in Detail
- Monitoring, Reporting, and Alerting Mechanisms
- Advanced Integration: Microsoft Defender and DLP Alerts
- Best Practices for a Successful DLP Implementation
- Additional Resources and Next Steps
- Conclusion
1. Introduction to Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Organizations today must balance the need to share information with the imperative to protect sensitive data. Whether the data is stored in emails, shared across collaboration platforms, or resides on local and cloud-based systems, the risk of oversharing or unauthorized access is ever-present.
What is DLP?
Data Loss Prevention is a set of practices, policies, and technologies that work together to ensure that sensitive information is not leaked or misused. Rather than merely scanning text for keywords, modern DLP solutions rely on deep content analysis. This involves using sophisticated algorithms and machine learning techniques to detect patterns that indicate sensitive data—ensuring that even nuanced or embedded data elements are recognized and protected.
Why is DLP Important?
Risk Reduction: Prevent inadvertent exposure of confidential information.
Regulatory Compliance: Help organizations meet stringent compliance requirements, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS.
Business Continuity: Minimize disruptions caused by data breaches, which can result in operational setbacks and reputational damage.
User Awareness: Educate users about secure data handling practices by providing real-time alerts and guidance during potentially risky activities.
2. How Modern DLP Works
Modern DLP solutions go far beyond simple keyword matching. They use a combination of techniques to ensure that sensitive data is identified accurately and in context. Here’s a deeper look at these techniques:
Deep Content Analysis
Primary Data Matching:
DLP systems first search for primary identifiers within a document—keywords, numeric patterns (such as credit card numbers or Social Security numbers), and other signature data. This initial scan is crucial in flagging content that could be sensitive.Regular Expression Evaluation:
By using regular expressions, DLP tools can detect data that adheres to certain formats. For example, patterns for bank account numbers, phone numbers, or other standardized codes can be identified even if they are interwoven with other text.Internal Function Validation:
Beyond pattern matching, DLP systems apply internal rules to validate whether the detected information truly qualifies as sensitive. This may include checksum validations or logic-based tests to differentiate between genuine data and false positives.Proximity Analysis:
Sometimes, the context of the data is as important as the data itself. DLP can detect when sensitive elements appear near each other—what we call secondary matches—to assess the overall risk of a data set.Machine Learning Algorithms:
Leveraging machine learning, DLP solutions continually improve their accuracy. Over time, these systems learn to better recognize subtle variations of sensitive data across diverse formats and content types.
This multifaceted approach helps ensure that DLP policies capture critical information accurately, reducing false positives while ensuring that sensitive data is not overlooked.
3. The Role of Microsoft Purview in Data Protection
Microsoft Purview serves as a comprehensive suite for data governance and compliance. DLP is a key component of this ecosystem, enabling organizations to enforce data protection policies seamlessly across multiple platforms.
Microsoft Purview DLP Capabilities
Cross-Platform Coverage:
Purview DLP extends its reach across various Microsoft 365 services, including Exchange, Teams, SharePoint, and OneDrive. It also integrates with Office applications (Word, Excel, PowerPoint), ensuring that content created or stored across the enterprise is continuously monitored.Endpoint and Device Support:
In addition to cloud services, Microsoft Purview supports data protection on local devices running Windows 10, Windows 11, and the latest macOS versions. This means that sensitive data remains safeguarded whether it is in transit or at rest on user devices.Non-Microsoft Cloud and On-Premises Integration:
For organizations that leverage a mix of cloud services, Purview DLP also monitors non-Microsoft cloud applications and on-premises file shares. This hybrid approach ensures consistent protection across all data environments.Advanced Platforms:
With the inclusion of tools like Fabric, Power BI workspaces, and even preview features like Microsoft 365 Copilot, Purview DLP covers a broad spectrum of environments, aligning with modern enterprise data flows.
By centralizing data protection within Microsoft Purview, organizations can enforce consistent DLP policies while benefiting from a unified management interface.
4. Preparing to Implement DLP: Pre-Implementation Essentials
Before diving into policy creation and deployment, it is important to establish a solid foundation. This involves understanding the key components of DLP and reviewing essential documentation provided by Microsoft.
Core Pre-Implementation Resources
Introduction to DLP Concepts:
Familiarize yourself with the basic principles of data loss prevention, including the methods used to detect and mitigate risks.Licensing Requirements:
Check the Microsoft 365 Enterprise Plans and Service Descriptions to understand which licensing options include full DLP capabilities. If you’re not an E5 customer, consider the 90-day trial for Microsoft Purview solutions to explore its full range of features.Related Articles and Guides:
Prior to launching a DLP initiative, review a series of core articles covering topics such as administrative units, planning for DLP, policy design, and deployment best practices. These guides provide step-by-step instructions to help you configure and manage your DLP policies effectively.
By reviewing these foundational materials, organizations can ensure that their DLP implementations are built on a well-informed strategy.
5. Developing a DLP Strategy: Planning for Success
A robust DLP program starts with thorough planning. This phase is critical not only for technical implementation but also for aligning the solution with your organization’s overall data security strategy.
A. Stakeholder Identification and Involvement
Engage Key Stakeholders:
Identify the teams and individuals who will be affected by the DLP policies. This typically includes IT administrators, security personnel, compliance officers, and business process owners.Define Roles and Responsibilities:
Assign clear responsibilities for policy creation, monitoring, and enforcement. Involve business leaders to help set realistic expectations and ensure that DLP measures align with business objectives.
B. Defining Sensitive Data Categories
Classify Data Types:
Determine which categories of data need protection. This might include financial records, proprietary information, personally identifiable information (PII), and confidential business data.Set Protection Priorities:
Not all data carries the same level of risk. Prioritize data based on sensitivity and the potential impact of a breach.
C. Setting Goals and Objectives
Security and Compliance Goals:
Establish clear, measurable objectives for your DLP program. Goals might include reducing the risk of data breaches, ensuring regulatory compliance, or increasing user awareness of secure data practices.Strategic Roadmap:
Create a roadmap that outlines the key phases of your DLP implementation—from initial planning and testing to full-scale deployment and continuous improvement.
D. Developing Policy Frameworks
Draft Policy Statements:
Begin by outlining what each policy is intended to achieve. Define acceptable user behaviors and clearly state the consequences of non-compliance.Tailor Policies to Business Processes:
Work with business process owners to understand how data flows through the organization. Adapt policies to ensure they support rather than hinder daily operations.
By taking a comprehensive approach to planning, you lay the groundwork for a DLP strategy that is both effective and aligned with your organization’s unique needs.

(from Microsoft website)
6. Preparing Your Environment for DLP Deployment
The next step is ensuring that your technological environment is ready to support DLP policies. This involves verifying that all endpoints, applications, and storage systems are configured to interact seamlessly with Microsoft Purview.
A. Assessing Data Repositories and Workloads
Cloud Services:
Ensure that Microsoft 365 services (Exchange, Teams, SharePoint, OneDrive) are configured correctly. Each service may have its own prerequisites and settings for DLP integration.Office Applications:
Verify that Office applications such as Word, Excel, and PowerPoint are updated and compatible with DLP policies.Endpoints:
Confirm that devices running Windows 10, Windows 11, and the latest macOS versions are compliant with DLP requirements. This may include ensuring that operating system updates and necessary security patches are applied.
B. On-Premises and Hybrid Environments
File Shares and Local Repositories:
For on-premises file shares and SharePoint servers, prepare for the deployment of Microsoft Purview Information Protection scanners. These tools help extend DLP coverage to systems that are not natively part of Microsoft 365.Hybrid Deployments:
If your organization uses a mix of cloud-based and on-premises systems, ensure that both environments are configured to send data to a central DLP monitoring system. This will help maintain a consistent policy across all data sources.
C. Testing and Simulation
Draft Policies in Simulation Mode:
Before enforcing policies that block actions, run them in simulation mode. This allows you to observe how policies would affect user behavior without actually restricting access.Validate Environment Readiness:
Use test accounts and pilot groups to ensure that data flows correctly into the DLP system. Monitor how different workloads—whether email, file sharing, or endpoint data—interact with the proposed policies.
Properly preparing your environment is crucial to a successful DLP deployment. It minimizes disruptions and helps identify potential issues before policies go live.
7. Deploying and Fine-Tuning DLP Policies
Once your environment is prepared and your planning is complete, it’s time to deploy your DLP policies. A phased rollout—starting with simulation and gradually moving to full enforcement—ensures a smooth transition and allows you to adjust policies based on real-world results.
A. Policy Design and Initial Deployment
Define Control Objectives:
Clearly outline the security objectives for each DLP policy. Identify which data types need protection, and determine the contexts in which sensitive data might be exposed.Create a Draft Policy:
Use the Microsoft Purview compliance portal to create a policy draft. Start with a single workload or data repository if you prefer a focused rollout, or apply a broader policy to test across multiple services simultaneously.Simulation Mode Testing:
In simulation mode, policies log events without enforcing restrictions. This allows you to capture how users interact with sensitive data and observe any false positives or missed detections. Monitor the logs and reports carefully to refine your policies.
B. Monitoring and Policy Adjustment
Analyze Policy Impact:
Use the reporting tools available in Microsoft Purview to review audit logs and activity explorer results. Identify any patterns where policies might be too strict or too lenient.Adjust Conditions and Thresholds:
Fine-tune the policy rules by modifying conditions such as the number of sensitive items detected, the context in which data appears, and the actions triggered by a match. For example, you might adjust thresholds to reduce alerts on benign activities while still catching truly risky behavior.Engage with End Users:
Use policy tips and user notifications to educate users about the new rules. Allow for feedback to understand how policies affect everyday workflows. This feedback loop is vital for maintaining a balance between security and user productivity.
C. Enabling Full Enforcement
Transition to Enforcement Mode:
Once simulation testing confirms that policies meet your control objectives without excessive disruption, enable full enforcement. Note that policy changes may take up to an hour to propagate fully across the system.Monitor Live Activity:
Continue to monitor the system closely after enforcement. Keep an eye on user behavior, false positives, and any incidents reported. Fine-tuning is an ongoing process as data environments evolve and new threats emerge.Regular Reviews and Updates:
Schedule periodic reviews of your DLP policies. As new types of sensitive information or regulatory requirements arise, update your policies accordingly. This continuous improvement cycle is critical to maintaining robust data protection over time.
8. Configuring Your DLP Policies in Detail
A DLP policy in Microsoft Purview is highly configurable, giving you the flexibility to tailor it to your organization’s specific needs. Below is a detailed walkthrough of the configuration process:
A. Selecting What to Monitor
Predefined Templates vs. Custom Policies:
Microsoft Purview offers a variety of predefined templates—such as those for financial data, medical records, and privacy information across different regions. These templates provide a starting point for policy creation. Alternatively, you can build a custom policy that leverages sensitive information types (SIT), retention labels, and sensitivity labels specific to your organization.Determining Data Scope:
Decide whether the policy should cover all data repositories or only specific segments. For instance, you might focus on data in emails or files stored in SharePoint, based on the criticality of the data and the risk profile of each location.
B. Administrative Scoping
Defining User Groups and Units:
DLP policies can be scoped to specific user groups or administrative units. This means that administrators can manage policies for only the users they oversee. Scoping your policies helps ensure that sensitive data is protected in targeted areas without overwhelming the entire organization with a one-size-fits-all rule.Granular Control:
Use administrative scoping to differentiate policies between departments or business units. For example, the finance department may have stricter rules compared to other departments, reflecting the higher sensitivity of its data.
C. Setting Conditions and Triggers
Establishing Trigger Conditions:
Define the conditions that must be met for a DLP policy to be triggered. This might include specific data types, keywords, or even contextual clues such as the number of sensitive items being transmitted at once.Contextual Triggers:
Incorporate rules that trigger based on user behavior or contextual factors—for example, sending a high volume of data to an external recipient might trigger a policy even if the data itself is not inherently sensitive.Customization Options:
Adjust the rules to be as specific or broad as necessary. You can set policies that allow for user overrides with justification, or you can enforce strict blocking actions if the risk is deemed too high.
D. Defining Protective Actions
User Notifications and Policy Tips:
When a policy is triggered, one common action is to display a policy tip. This pop-up notification informs the user that their current action might expose sensitive data and advises on corrective steps.Blocking and Quarantine Measures:
Depending on the risk and context, the DLP policy can block the action outright. For stored data, the policy may move files to a secure quarantine location where they can be reviewed before being released or permanently secured.Application-Specific Actions:
For different platforms, the actions vary. For example, in Teams, the system might block the display of sensitive information in chat messages. On endpoints, it may prevent copying data to removable devices.
E. Saving and Deploying the Policy
Centralized Management:
Once configured, the policy is stored in a central policy repository within the Microsoft Purview compliance portal. From here, it is synchronized with all the connected data sources.Propagation and Activation:
After saving, the policy begins a synchronization process across Microsoft 365 services (including Outlook, OneDrive, SharePoint, and Teams), as well as endpoints and on-premises environments. Regular propagation intervals (often within an hour) ensure that new policies take effect quickly across the board.
By carefully configuring each element of your DLP policy, you ensure that your organization’s sensitive data is safeguarded in a manner that is both comprehensive and aligned with business needs.
9. Monitoring, Reporting, and Alerting Mechanisms
A vital component of any DLP strategy is the ability to continuously monitor and report on data protection activities. Microsoft Purview provides robust tools for tracking policy performance and user interactions with sensitive data.
A. Logging and Audit Trails
Centralized Logging:
Every time a DLP policy is triggered, the event is recorded in the Microsoft 365 Audit Log. This centralized log serves as the backbone for later investigations and compliance reporting.Detailed Event Data:
Each logged event includes metadata such as the user involved, the type of sensitive data detected, and the action taken by the policy (for example, a block or a user override).
B. Activity Explorer
User-Centric View:
The Activity Explorer tool allows administrators to filter and analyze DLP events across various dimensions—whether by endpoint activities, file modifications, or data egress incidents.Preconfigured Filters:
Out-of-the-box filters help you quickly view events such as “Files containing sensitive info types” or “Egress activities.” These filters are designed to provide a comprehensive picture of data movement and policy enforcement.Contextual Analysis:
With Activity Explorer, you can view contextual summaries around sensitive data matches. This might include adjacent text that gives further insight into the risk level of the activity.
C. Alerts and Incident Response
Real-Time Alerts:
When a policy violation occurs, Microsoft Purview can generate an alert in real time. These alerts are visible in dedicated dashboards, allowing administrators to quickly assess and respond to potential risks.Integrated Investigation Tools:
DLP alerts are further integrated with Microsoft Defender portals, enabling a streamlined process for investigating incidents. Administrators can access detailed metadata, review related user activities, and even change the investigation status of each alert.Alert Retention and Management:
Alerts have specific retention periods—for instance, DLP alerts may be available in Microsoft Defender for up to six months, but only for 30 days within the Purview dashboard. Understanding these retention periods is crucial for planning investigations and audits.
D. PowerShell Reporting Cmdlets
Advanced Reporting Options:
For those who prefer script-based interactions, Microsoft Purview supports various PowerShell cmdlets to extract detailed DLP reports. Commonly used commands include:Get-DlpDetailReportGet-DlpDetectionsReportGet-DlpSiDetectionsReport
Cross-Service Data Aggregation:
Some cmdlets pull data across multiple Microsoft 365 services (including Exchange and on-premises repositories), providing a holistic view of DLP activity.
These reporting and alerting mechanisms are essential for both reactive and proactive security measures—allowing your organization to not only respond to incidents but also continually refine your DLP policies.
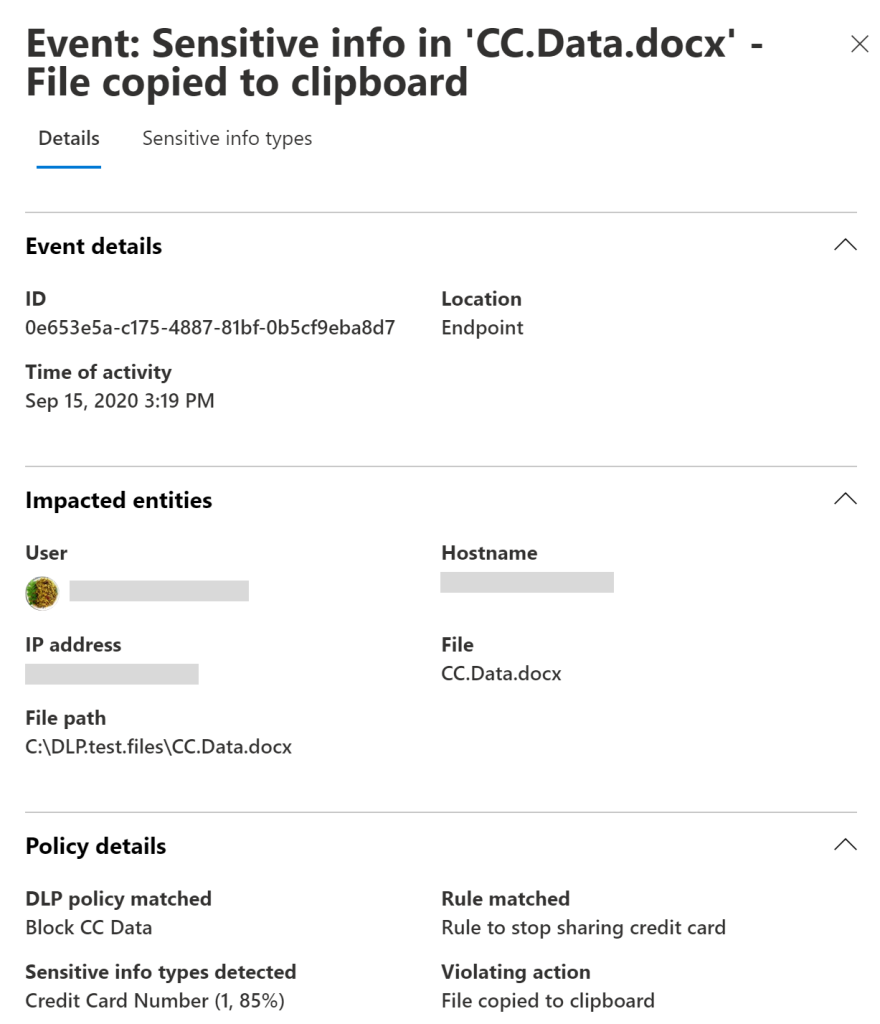
(from Microsoft website)
10. Advanced Integration: Microsoft Defender and DLP Alerts
As data environments become increasingly complex, integrating DLP with broader security tools can provide an extra layer of protection. Microsoft Purview works closely with Microsoft Defender to offer a seamless security experience.
A. Integration with Microsoft Defender
Unified Dashboard Experience:
DLP alerts generated by Purview are also forwarded to the Microsoft Defender portal. This integration means that administrators have access to a single dashboard for both DLP incidents and broader security alerts.Enhanced Incident Investigation:
Microsoft Defender’s tools allow for deeper analysis of each DLP event. From investigating user actions to examining the metadata around a policy match, Defender provides a more granular level of detail.Correlated Threat Detection:
By correlating DLP events with other security data, Microsoft Defender can help identify larger patterns of potential data exfiltration or coordinated attacks. This holistic view enables faster and more effective incident response.
B. Contextual Analysis and Egress Monitoring
User Egress Activities:
One of the key features of DLP is its ability to monitor when sensitive data is being moved outside the organization. Whether a user is copying data to an external drive, sending an email to an unapproved recipient, or uploading files to a suspicious domain, these actions are flagged for review.Contextual Summaries:
For each flagged event, DLP can provide a contextual summary that includes surrounding text or activity logs. This information is critical for understanding the full scope of a potential data breach.Endpoint-Specific Considerations:
For endpoints such as Windows 10, Windows 11, and macOS devices, ensure that all necessary patches (for example, KB5016688 for Windows 10 and KB5016691 for Windows 11) are applied. These updates help optimize the performance of DLP monitoring on local devices.
By leveraging the advanced integrations available through Microsoft Defender, your organization can benefit from a unified, comprehensive security strategy that goes well beyond traditional DLP measures.
11. Best Practices for a Successful DLP Implementation
A well-designed DLP strategy not only relies on technology but also on sound business practices and ongoing user engagement. Here are some best practices to help you achieve lasting success with your DLP program:
A. Training and User Awareness
Employee Education:
Regularly train employees on how to handle sensitive data and the importance of following DLP guidelines. Educate them about the potential risks and the rationale behind the implemented policies.Clear Communication:
Use policy tips and in-application notifications to remind users of best practices. When users understand why certain actions are blocked, they are more likely to comply and adjust their behavior.
B. Phased Rollout and Continuous Improvement
Start with Simulation:
Always begin your DLP deployment in simulation mode to observe and analyze real-world behavior without immediately restricting user actions. This phased approach minimizes business disruption.Iterative Adjustments:
Use feedback from simulation mode to refine your policies. Continue to monitor performance even after moving to full enforcement, and be prepared to adjust rules as business needs evolve.
C. Balancing Security with Productivity
Avoid Over-Blocking:
While protecting data is critical, overly restrictive policies can hinder productivity. Aim for a balanced approach that protects sensitive information while allowing users to perform their tasks efficiently.Context-Based Policies:
Consider creating context-aware rules that take into account the nature of the task at hand. For example, allow certain sharing actions internally while restricting external communications.
D. Regular Reviews and Audits
Scheduled Policy Audits:
Periodically review your DLP policies and the associated logs. This helps identify any gaps or evolving risks that require policy adjustments.Stay Informed:
Keep up with the latest best practices in data protection, as well as updates from Microsoft regarding Purview enhancements. The threat landscape is constantly evolving, so your policies should evolve as well.
By incorporating these best practices, your organization can maintain a dynamic and effective DLP strategy that safeguards data without impeding day-to-day operations.
12. Additional Resources and Next Steps
For organizations looking to expand their knowledge and refine their DLP implementations, Microsoft Purview offers a wealth of additional resources and tools:
A. Further Reading and Learning Materials
Endpoint Data Loss Prevention:
Explore guides and tutorials on how to implement DLP measures specifically for endpoints, ensuring that mobile and desktop devices are secure.DLP in Collaboration Platforms:
Learn about specific policies for Microsoft Teams, SharePoint, and OneDrive. Each platform may require unique configurations to address its particular data-sharing risks.On-Premises Scanner Setup:
For organizations that rely on local file repositories, review the detailed steps for deploying the Purview Information Protection scanner. This tool is crucial for extending DLP coverage to on-premises environments.
B. Regulatory Compliance and Privacy
Data Privacy Regulations:
Understand how DLP policies can help you comply with regional and international data privacy laws, such as GDPR or HIPAA. Detailed guides are available to help map policy configurations to compliance requirements.Integration with Compliance Frameworks:
Microsoft Purview is designed to integrate seamlessly with other compliance tools, ensuring that your data protection efforts contribute to a broader regulatory strategy.
C. Community and Support
User Forums and Communities:
Engage with other IT professionals and data security experts through online communities and forums. Sharing experiences and best practices can help you refine your DLP approach.Microsoft Support Resources:
Access official documentation, training modules, and customer support channels provided by Microsoft. These resources can be invaluable when troubleshooting issues or seeking advice on advanced configurations.
D. Planning Your Next Steps
Pilot Programs:
If you haven’t already, consider launching a pilot program within a small department or a limited scope. This will provide real-world feedback before rolling out policies organization-wide.Roadmap Development:
Develop a long-term roadmap for your DLP strategy. This should include regular reviews, updates based on new threats, and expansion plans to cover additional data repositories as needed.
Conclusion
In an age where data is one of the most valuable—and vulnerable—assets, a comprehensive Data Loss Prevention strategy is essential. Microsoft Purview provides a robust platform that not only helps you detect and protect sensitive information but also integrates seamlessly with your broader data governance and compliance framework.
By carefully planning, preparing your environment, and deploying well-crafted policies, your organization can effectively safeguard sensitive data across email, collaboration platforms, endpoints, and on-premises repositories. The continuous monitoring, detailed reporting, and alerting mechanisms ensure that you have full visibility over your data flows, enabling proactive management of potential risks.
Moreover, integrating DLP with tools like Microsoft Defender offers an added layer of security by correlating alerts across the entire ecosystem—ensuring that even sophisticated attempts at data exfiltration are detected and mitigated.
As organizations continue to navigate an increasingly complex digital landscape, investing in a thoughtful, well-implemented DLP strategy is not just a regulatory requirement—it is a critical component of modern business resilience. Through ongoing training, regular policy reviews, and a commitment to balancing security with operational efficiency, your organization can build a culture of data protection that stands the test of time.
For more detailed insights and advanced configurations, be sure to explore the additional resources provided by Microsoft Purview and engage with the broader community of data security professionals. With the right tools and a proactive mindset, you can create a secure environment where sensitive data is protected at every step of its lifecycle.

© 2026 ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
Sitemap
Get in touch today.
For any questions
