![]()
Microsoft Copilot, Gen AI and ROT Data Management
The whitepaper Gen AI and ROT Data Management, co‑authored by Infotechtion’s Vebjørn Krågebakk, and BI Norwegian Business School Professors Christoph Lutz and Samson Yoseph Esayas makes a clear case: if you want reliable, safe and efficient Gen AI, you need disciplined and consistent data lifecycle management and decisive ROT reduction. Moreover, the impact of ROT data on an organization’s economy is considerable as storage of data is expensive and its environmental impact contributes to as much as 1.47% of all global greenhouse gas emissions. This blog post examines the whitepaper’s key findings in an easy-to-read format, so stay tuned!
What Is ROT— And Why It Matters Now
Redundant, Obsolete and Trivial (ROT) is information that is duplicated, outdated, or is generally considered to have little to no organizational value. Examples include duplicated attachments in emails, files with outdated information that has lost its value, meeting notes, half-finished drafts and the pictures you used for a presentation two years ago and more. Let’s be honest, people are good at creating data but not deleting it. The beforementioned whitepaper describes how as much as 70% of all organizational data can be classified as ROT. This data clutters repositories, inflates storage and discovery costs, and pollutes the input data for Gen AI. This leads to confusing, conflicting, or flat‑out wrong outputs.

Imagine a scenario where you ask Microsoft Copilot to fetch sales data from last month for a particular customer. However, employees handling sales data often duplicate items so invoices and orders exist in multiple versions in several locations. Faced with such scenarios, Microsoft Copilot and similar tools use metadata to help distinguish and try to find the correct version but errors still occur at high percentages. This scenario is one that organizations face every day, reducing both the effectiveness of AI and the end users’ trust in their AI tools.

How Big Is The Problem?
Field observations and previously published research summarized in the whitepaper show that 54–80% of enterprise content can be classified as ROT (average 70.8%), with reuse probability of most files dropping below 1% after 30 days. Duplicates and abandoned drafts don’t just slow people down; they degrade model quality and trust in AI‑assisted work.
ROT has a measurable financial curve, too. Using realistic Microsoft 365 storage assumptions, modeled over‑storage at a 25% annual growth crosses 1M USD within ~8.5 years for a 10k‑employee organization, reaching 5.67M USD cumulative over a decade. These costs are based on overstorage along, not accounting eDiscovery, incident response, or opportunity costs.
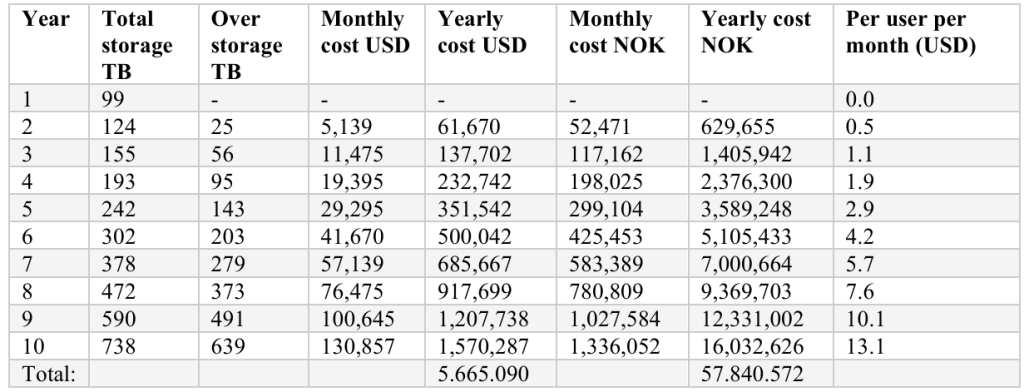
The Sustainability Angle
Data at rest is never truly “at rest.” The compute, replication, and cooling that keep ROT alive consume energy and add to emissions. Based on estimations and available statistics, the whitepaper deduces that ROT may account for ~1.47% of global Greenhouse Gas emissions. The level at which ROT is expected to grow with access to gen AI tools that has made data production easier than ever, is alarming.

ROT through the compliance lens: AI Act and GDPR
Redundant, Obsolete and Trivial data collide with both national and international regulatory expectations. For instance, the GDPR’s minimization and accuracy principles require organizations to retain only what’s necessary (minimization) and for a limited duration. The AI Act’s data quality requirements demand accurate and up-to-date data. Safe to say, ROT poses a significant noncompliance threat to organizations as generative AI may use dated and excessively stored data for its output. These outputs can also resurface old data and expose organizations’ noncompliant disposition and disposal practices. As a result, serious financial loss can occur.
Microsoft Copilot and other Gen AI solutions thrive on good data
When organizations allow Redundant, Obsolete, and Trivial (ROT) data to accumulate, they introduce significant risks to the accuracy and reliability of Generative AI outputs. For Microsoft Copilot—whose effectiveness depends on quality, current, and relevant enterprise data—surges of ROT content mean prompts are more likely to return outdated, duplicate, or misleading information. The same threats apply to other Gen AI tools: when the underlying data estate is cluttered with ROT, AI models can surface irrelevant documents, perpetuate inaccuracies, and erode trust in AI‑assisted recommendations.
According to findings in the referenced Whitepaper, up to 70% of enterprise content can be classified as ROT. This means that every time Copilot or any Gen AI tool is prompted, there’s a high probability it will draw from non‑essential or outdated data—diluting the value of its insights and increasing the risk of errors.
How to address ROT and data lifecycle management
To effectively reduce ROT and strengthen data management processes, organizations should begin by defining ROT in their local context. The Gen AI and Rot Data Management whitepaper shows that data with high velocity and volume lose its relevancy quicker than other comparable data. Once data has passed the 30-day mark, less than 1 percent of data will ever be used again. By analyzing trends of access and reusability, organizations can use this information to create retention policies and labels for effective disposal of ROT.
Using Microsoft Copilot and other Gen AI tools should rightfully be celebrated because it enhances productivity – but the flipside is that producing data has now become easier than ever. The access to these productivity tools is likely to expedite the growth of ROT, further demanding effective data management. Microsoft Purview addresses data lifecycle management such as ROT data management, and it has built-in capabilities to effectively address the growing data created by Copilot and other AI tools. Through solutions such as “Data Security Posture Management” (DSPM) for artificial intelligence, organizations can create retention labels for generative AI input and output – effectively remediating the growth of ROT from an AI perspective. For tech-savvy people, it is worth noting that DSPM for AI in Purview works as a quick access tool for accessing multiple AI resources scattered throughout Purview’s Data Loss Prevention, Data Lifecycle Management, Information Protection, Communication Compliance and Insider Risk Management capabilities and solutions.
While Microsoft Purview is an excellent tool for data lifecycle management, it has some limited capabilities. As for data management, this is especially true in case of data disposal. Infotechtion’s I-ARM help by extending Purview’s native capabilities in data lifecycle management, helping managing data at scale. Feel free to read more about I-ARM on Infotechtion’s website. A link is provided in the References below.
View the full Whitepaper
This blog condenses the key arguments and evidence from our new whitepaper. For the full analysis—including the data reuse curve, long‑term cost model, compliance mapping, and the sustainability calculation—download and read the whitepaper at Research Gate and SSRN. Both are attached in the References below.
If you’re ready to make GenAI safer and more effective by shrinking ROT at the source—while strengthening compliance and cutting storage spend—our team can help operationalize Microsoft Purview with or without i‑ARM to turn policy into measurable outcomes. Contact Infotechtion at contact@infotechtion.com
References
Infotechtion (2025). AI Governance. Accessed: https://infotechtion.com/ai-governance/
Krågebakk, V., Lutz C. & Esayas S. (2025). Research Gate. Gen AI and Rot Data Management. Accessed: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/395255386_Gen_AI_and_ROT_Data_Management?channel=doi&linkId=68b960693391fb1a7a4d5172&showFulltext=true
Krågebakk, V., Lutz C. & Esayas S. (2025). SSRN. Gen AI and Rot Data Management. Accessed: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5439179



